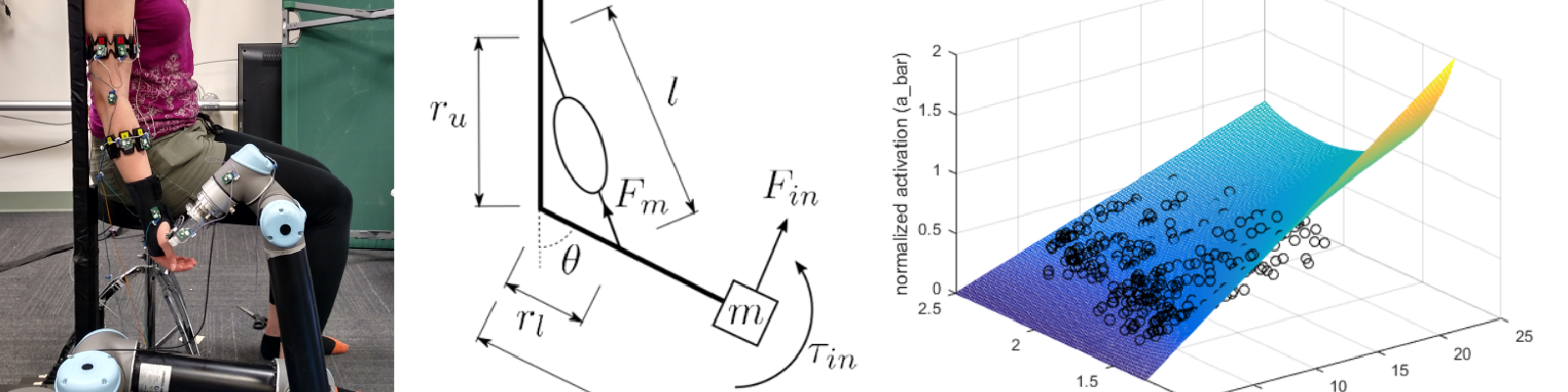
 Left: Collection of sEMG, force, and motion capture data. Center: Simplified model of the elbow joint used in modeling. Right: Muscle force models can be fitted to a given subject via collection of activation, force, and angle data.
Left: Collection of sEMG, force, and motion capture data. Center: Simplified model of the elbow joint used in modeling. Right: Muscle force models can be fitted to a given subject via collection of activation, force, and angle data.
Sensor-Driven Musculoskeletal Dynamic Modeling
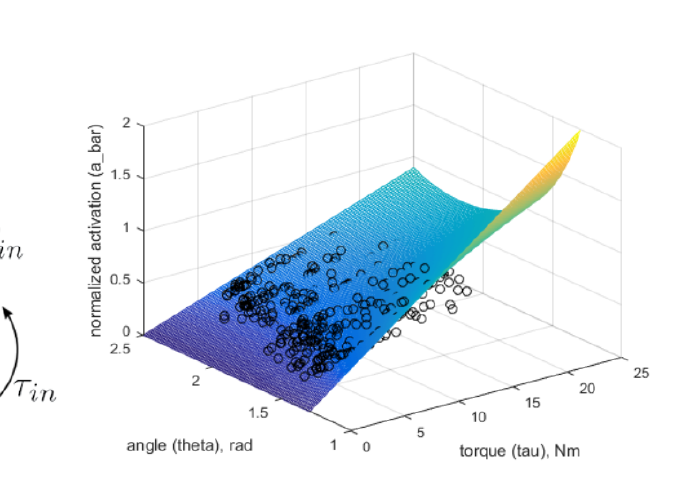 Left: Collection of sEMG, force, and motion capture data. Center: Simplified model of the elbow joint used in modeling. Right: Muscle force models can be fitted to a given subject via collection of activation, force, and angle data.
Left: Collection of sEMG, force, and motion capture data. Center: Simplified model of the elbow joint used in modeling. Right: Muscle force models can be fitted to a given subject via collection of activation, force, and angle data.
Sensor-Driven Musculoskeletal Dynamic Modeling
Abstract
The creation of a human dynamical model useful in upper-limb exoskeleton control remains an open problem. We present a framework that approaches model generation from a “sensor-driven” design perspective that explicitly avoids over- fitting parameters and minimally relies on literature values and biological assumptions. Initial results on synthetic data for a simplified model of the elbow indicate that this framework is a viable starting point from which to build more sophisticated dynamical models. Full results can be found in Tech Rep. UCB/EECS-2016-66.
Type
Publication
In International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), IEEE.
Date
August, 2016
